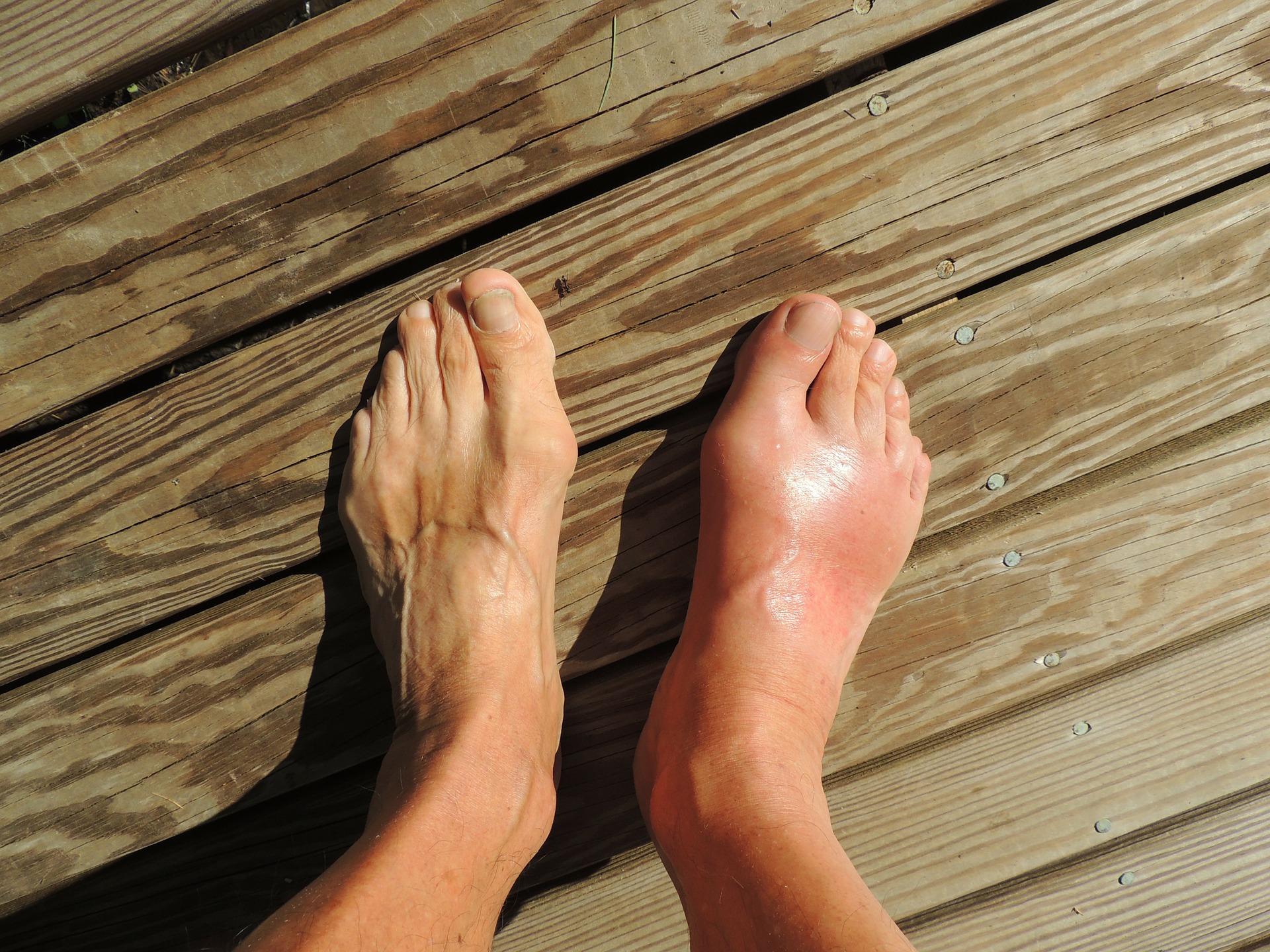
Gout is a common form of arthritis that is identified by sudden and severe pain in the joints, accompanied by swelling and redness. The joint most commonly affected by gout is the base of the big toe on either foot.
Symptoms often come on at night and appear without warning. Signs to watch for include: inflammation, redness, and intense pain in the joint. Contacting a doctor the next day is preferable, however, seek immediate medical attention if the joint becomes hot and inflamed as this can indicate the presence of an infection.
The cause of gout comes from a build-up of uric acid which can form crystals in your joints and cause intense pain. Although your body can usually handle the normal input of uric acid in the body, sometimes things get out of balance, such as when your diet consists mainly of meat, seafood, and beer.
Other risks for developing gout include: obesity, family history, if you’re between the ages of 30-50, and if you’re male or a woman in menopause. Certain medications can also increase your risk of gout.
Preventing gout can be simple with a few diet changes such as drinking plenty of water and avoiding sugary drinks and alcohol. Rather than having a lot of meat and fish as your protein, get your protein from low-fat dairy products or nuts.
A variety of medications are available to assist people affected by gout, including over the counter medications such as Advil and Motrin IB. Prescriptions for drugs such as Celebrex need to be recommended by a doctor. Corticosteroids are also available to patients who are unable to take traditional medications for any number of health reasons.

Comments